The following auditing interpretation is not the current version and does not reflect any amendments effective on or after December 31, 2016. The current version of the auditing interpretations can be found here.
AU Section 9342
Auditing Accounting Estimates: Auditing Interpretations of Section 342
1. Performance and Reporting Guidance Related to Fair Value Disclosures
.01
Question—In December 1991, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Statement No. 107, Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments [AC section F25], which requires all entities to disclose the fair value of certain financial instruments for which it is practicable to estimate fair value. Some entities may disclose the information required by FASB Statement No. 107 and also disclose voluntarily the fair value of assets and liabilities not encompassed by FASB Statement No. 107. What are the auditor's responsibilities in situations in which entities are disclosing required or both required and voluntary fair value financial information?
.02
Interpretation—The auditor should determine whether the fair value disclosures represent only those required by FASB Statement No. 107 or whether additional voluntary fair value information has been disclosed by the entity. When auditing management's estimate of both required and voluntary fair value information, the auditor should obtain sufficient appropriate evidential matter to reasonably assure that—
- the valuation principles are acceptable, are being consistently applied, and are supported by the underlying documentation, and
- the method of estimation and significant assumptions used are properly disclosed.
If such assurance cannot be obtained, the auditor should evaluate whether the financial statements are materially affected by the departure from generally accepted accounting principles.
.03
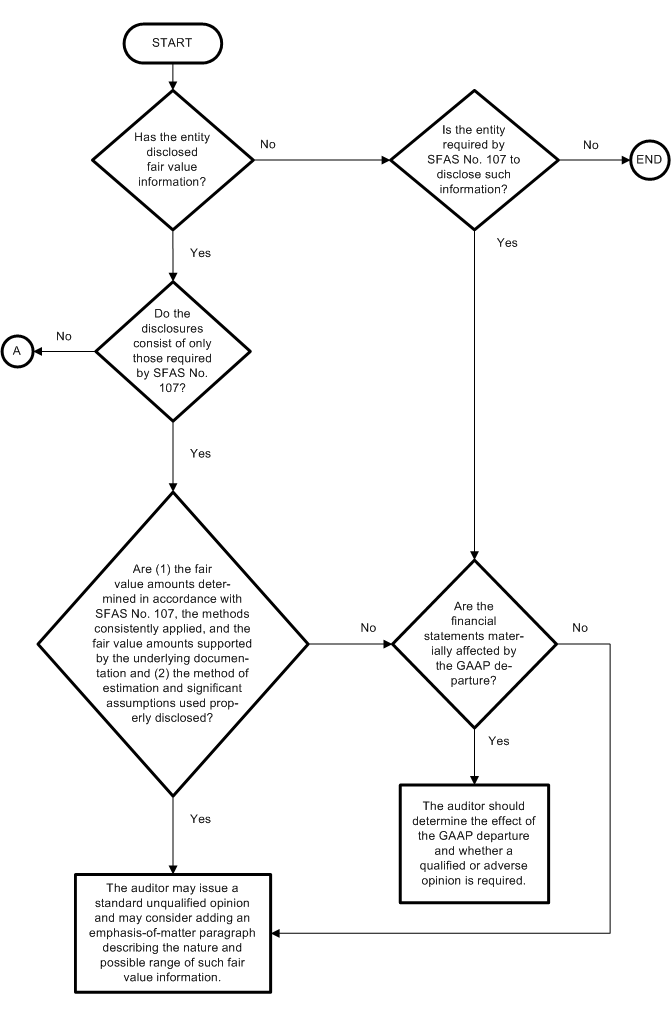
Required Information Presented—When an entity discloses in its basic financial statements only information required by FASB Statement No. 107, the auditor may issue a standard unqualified opinion (assuming no other report modifications are necessary). The auditor may add an emphasis-of-matter paragraph describing the nature and possible range of such fair value information especially when management's best estimate of value is used in the absence of quoted market values (FASB Statement No. 107, paragraph 11 [AC section F25.115D]) and the range of possible values is significant. If the entity has not disclosed required fair value information, the auditor should evaluate whether the financial statements are materially affected by the departure from generally accepted accounting principles.
.04
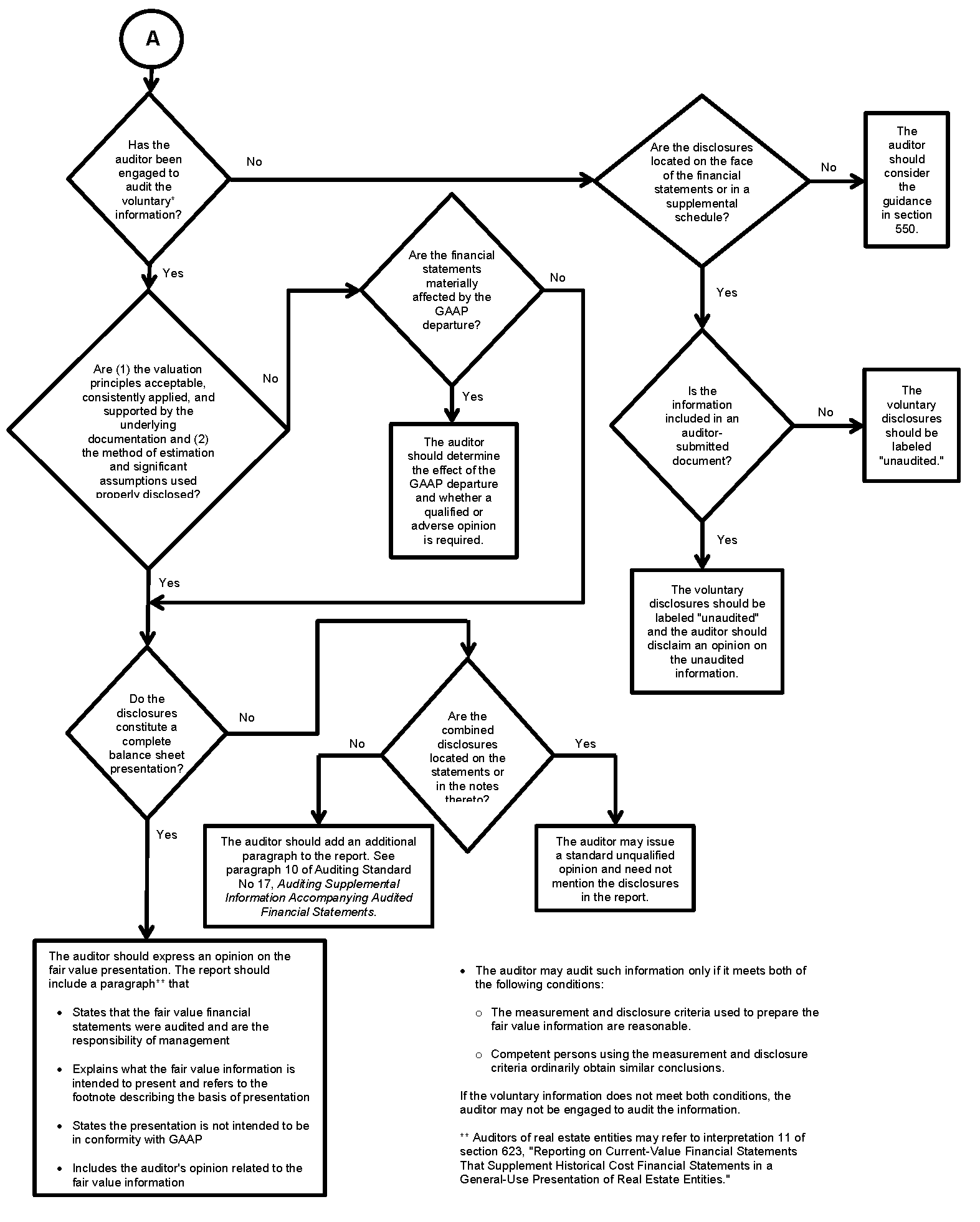
Required and Voluntary Information Presented—When voluntary information is presented in addition to required information the auditor may audit the voluntary information only if both the following conditions exist:
- the measurement and disclosure criteria used to prepare the fair value financial information are reasonable
- competent persons using the measurement and disclosure criteria would ordinarily obtain materially similar measurements or disclosures.
In applying this guidance to fair value disclosures, the intention is that another auditor would reach similar conclusions regarding the reasonableness of the valuation or estimation techniques and methods used by the entity.
.05
Voluntary disclosures may supplement required disclosures in such a fashion as to constitute either a complete balance sheet (the fair value of all material items in the balance sheet) or a presentation of less than a complete balance sheet.
.06
When the audited disclosures constitute a complete balance sheet presentation, the auditor should add a paragraph to the report, similar to the following:
We have also audited in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America the supplemental fair value balance sheet of ABC Company as of December 31, 20XX. As described in Note X, the supplemental fair value balance sheet has been prepared by management to present relevant financial information that is not provided by the historical-cost balance sheets and is not intended to be a presentation in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. In addition, the supplemental fair value balance sheet does not purport to present the net realizable, liquidation, or market value of ABC Company as a whole. Furthermore, amounts ultimately realized by ABC Company from the disposal of assets may vary significantly from the fair values presented. In our opinion, the supplemental fair value balance sheet referred to above presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein as described in Note X.
.07
When the audited disclosures do not constitute a complete balance sheet presentation and are located on the face of the financial statements or in the footnotes, the auditor may issue a standard unqualified opinion and need not mention the disclosures in the report. When the audited disclosures do not constitute a complete balance sheet presentation and are included in a supplemental schedule or exhibit, the auditor should look to the requirements in Auditing Standard No. 17, Auditing Supplemental Information Accompanying Audited Financial Statements.
.08
In some situations, the auditor may not be engaged to audit the voluntary information or may be unable to audit it because it does not meet both conditions in paragraph .04 of this interpretation. If the unaudited voluntary disclosures are located on the face of the financial statements or in the footnotes, the voluntary disclosures should be labeled "unaudited." If the unaudited information is presented in a supplemental schedule, the voluntary disclosures should be labeled "unaudited" and the auditor should disclaim an opinion on the unaudited information.
.09
When the unaudited voluntary disclosures are included in a client-prepared document and are located on the face of the financial statements, the footnotes, or in a supplemental schedule, the voluntary disclosures should be labelled "unaudited." When such unaudited information is not presented on the face of the financial statements, the footnotes, or in a supplemental schedule, the auditor should consider the guidance in section 550, Other Information in Documents Containing Audited Financial Statements.
.10
The auditing guidance related to each of these alternatives is presented in the following flowcharts:
AUDITING GUIDANCE FOR FAIR VALUE INFORMATION
Required fn * Information Only
AUDITING GUIDANCE FOR FAIR VALUE INFORMATION
Required and Voluntary Information
[Issue Date: February, 1993; Revised: October, 2000.]
Footnotes (AU Section 9342 — Auditing Accounting Estimates: Auditing Interpretations of Section 342):
fn * Required by Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 107, Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments.